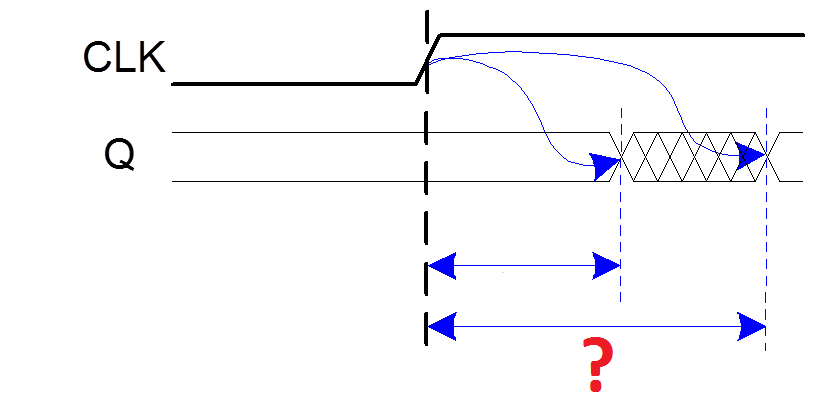
13. What kind of delay is illustrated on the picture below (marked by "?")?
a) Clock-to-Q Propagation delay:
tpcq = time after clock edge that the output Q is guaranteed to be stable (i.e., to stop changing)
b) Clock-to-Q Contamination delay:
tccq = time after clock edge that Q might be unstable (i.e., start changing)
c) Skew: difference between two clock edges. The clock doesn’t arrive at all registers at same time
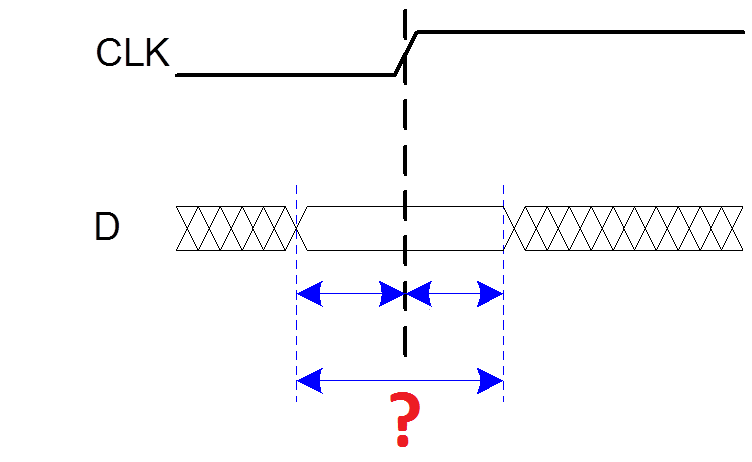
 14. What kind of timing constraint is illustrated on the picture below (marked by "?")?
a) Setup time: tsetup = time before clock edge data must be stable (i.e. not changing)
b) Hold time: thold = time after clock edge data must be stable
c) Aperture time: ta = time around clock edge data must be stable (ta = tsetup + thold)
d) Tc = minimum and maximum delays between registers
14. What kind of timing constraint is illustrated on the picture below (marked by "?")?
a) Setup time: tsetup = time before clock edge data must be stable (i.e. not changing)
b) Hold time: thold = time after clock edge data must be stable
c) Aperture time: ta = time around clock edge data must be stable (ta = tsetup + thold)
d) Tc = minimum and maximum delays between registers
 15. Which rule for signal assignment is violated in the following code?
a) Synchronous sequential logic: use always @(posedge clk) or always_ff @(posedge clk)
and nonblocking assignments (<=)
always_ff @ (posedge clk)
q <= d; // nonblocking
b) Simple combinational logic: use continuous assignments (assign…)
assign y = a & b;
c) More complicated combinational logic: use always @* or always_comb and blocking assignments (=)
d) Assign a signal in only one always statement or continuous assignment statement
e) This code does not violate any rules for signal assignment
module dut
(
input clk,
input [7:0] d,
output logic [7:0] q
);
always @(posedge clk)
if (d == 3)
q <= 4;
always @(posedge clk)
if (d == 7)
q <= 1;
endmodule
15. Which rule for signal assignment is violated in the following code?
a) Synchronous sequential logic: use always @(posedge clk) or always_ff @(posedge clk)
and nonblocking assignments (<=)
always_ff @ (posedge clk)
q <= d; // nonblocking
b) Simple combinational logic: use continuous assignments (assign…)
assign y = a & b;
c) More complicated combinational logic: use always @* or always_comb and blocking assignments (=)
d) Assign a signal in only one always statement or continuous assignment statement
e) This code does not violate any rules for signal assignment
module dut
(
input clk,
input [7:0] d,
output logic [7:0] q
);
always @(posedge clk)
if (d == 3)
q <= 4;
always @(posedge clk)
if (d == 7)
q <= 1;
endmodule